5 Ways AI Chatbots Are Redefining Customer Support in 2026
Posted on: December 17th 2025
Customer Support Is Changing Faster Than Anyone Expected
Think back for a moment. Just a few years ago, seeking help from a brand often meant waiting in long lines, recounting your story to multiple agents, and hoping the call wouldn’t drop halfway through. In 2026, that experience feels like a different era. Customers now expect quick answers, genuine understanding, and support that doesn’t make them jump through hoops or steal their time.
The biggest driver of this shift is a new generation of intelligent chatbots capable of highly personalized support and high-trust handoffs to agents beyond the bot. These are very different from the rigid, scripted versions people used to complain about. Today’s systems follow conversations naturally, keep track of context, and adjust their tone as the situation changes. In many cases, they can even anticipate what someone is likely to need next based on past interactions and behavior.
This has quietly changed the role of customer support. Instead of being seen only as a cost to be managed, it is becoming a meaningful contributor to loyalty, satisfaction, and long-term revenue.
Importantly, this evolution hasn’t pushed people out of the picture. Automation now handles repetitive tasks and simple requests, freeing human agents to focus on what they do best: empathy, nuanced judgment, and complex troubleshooting. Straive’s approach is built around that balance—using responsible technology, strong data foundations, and thoughtful design so that digital tools extend human capability rather than replace it.
Taken together, these shifts mark the beginning of a new standard for customer experience: faster, more precise, and, paradoxically, more human and reassuring than the systems they replaced.
1. Personalization That Actually Feels Human
We’ve all seen claims of “personalized support,” but in practice, it often felt like the same generic script with your name plugged in. New AI chatbots break that pattern. They learn from previous interactions, understand preferences, and adapt their tone based on the customer’s emotional cues.
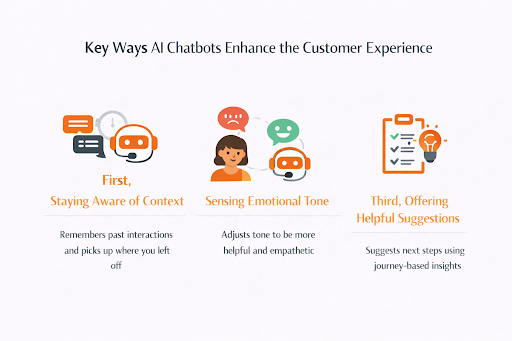
These improvements come from three abilities.
First, staying aware of context. A modern support bot doesn’t treat every interaction as a blank slate. It remembers earlier conversations, the channels you used, and the issues you raised. When you return, it can pick up where you left off instead of forcing you to repeat everything from the beginning. That continuity alone makes the experience feel more human and less transactional.
Second, sensing emotional tone. If a customer sounds frustrated, anxious, or confused, the system can respond more gently, simplify its language, and slow the pace of the interaction. When someone is relaxed or just exploring options, it can be more conversational and exploratory. This ability to adjust tone makes the interaction feel less like a script and more like a thoughtful conversation.
Third, offering helpful suggestions. Using journey-based insights, the chatbot can recommend renewals, upgrades, or relevant next steps that genuinely fit the situation. Done well, these nudges feel helpful rather than pushy because they are anchored in what the customer is actually trying to accomplish.
This kind of thoughtful personalization makes the conversation feel more like genuine assistance than automation. Straive organizes this approach into a repeating “Learning Loop”: collect insights, analyze them, personalize the response, and refine over time. The goal is simple—make every interaction more useful, more considerate, and more aligned with what the customer truly needs. Over time, that loop turns every interaction into training data, improving how well the system understands context, respects boundaries, and mirrors a brand’s service instincts.
2. Smooth, Connected Support Across Every Channel
Most customers don’t stay on one platform anymore. They might start with a quick question in a website chat, step away and continue the conversation in a mobile messaging app, and later follow up by email. In older support models, that behavior created a messy, disjointed trail—different agents, partial histories, and lots of “let me explain this again.”
Modern chatbot-driven support is designed to reduce that friction. Instead of treating each channel as a separate lane, the system pulls them together into one connected experience.
A key part of this is having a unified data system that standardizes after-contact note-taking, summarization, and reporting. Every channel—web, app, email, or messaging—draws from the same customer profile and interaction history. When someone switches from chat to email, the conversation doesn’t reset. The chatbot can see what was already discussed, what steps were taken, and what the customer is likely trying to do next. That continuity saves time for both sides and reduces frustration.
The messaging itself also adapts. The tone and structure that work in a website chat aren’t always ideal for a mobile message or an email. Modern systems adjust the style to match the channel while keeping the core meaning consistent. Short, quick exchanges feel natural on messaging apps, while email responses can be slightly more detailed and structured.
Multilingual intelligence plays a major role as well. Customers increasingly expect to communicate in the language they’re most comfortable with—and to be understood, not just translated. Straive’s multilingual framework is designed with that in mind. It focuses on preserving emotional tone, clarity, and intent, rather than just converting words literally.
The result is a support experience that feels consistent and familiar. Customers don’t need to repeat themselves, context isn’t lost when they move between devices, and the conversation sounds like it was written for them—not simply converted from somewhere else.
3. Automation That Actually Solves Things
One of the biggest shifts in modern customer support is that chatbots no longer just “talk about” problems—they can actually help solve them. Instead of stopping at FAQs or basic status checks, these systems now handle a wide range of tasks, from order updates and refunds to device troubleshooting and document verification. For customers, that means less waiting, less back-and-forth, and fewer handoffs that slow everything down.
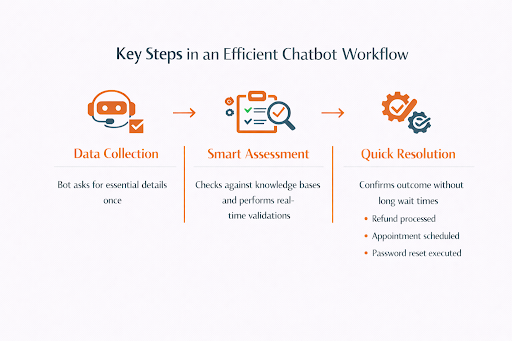
In a well-designed workflow, the process starts with data collection. The bot asks for only the details it truly needs—and it asks for them once, not repeatedly. It then compares the issue against existing knowledge bases, policies, and past cases to see what has worked before in similar situations. Wherever possible, it performs real-time checks, such as validating an order, confirming an account detail, or testing a configuration.
Only when all that is complete does it move to resolution. If the situation is straightforward and falls within established rules, the chatbot can confirm the outcome on the spot: a refund processed, an appointment scheduled, a password reset completed, a troubleshooting step executed. The customer gets closure without sitting in a long queue or retelling the story to multiple people.
Crucially, this doesn’t mean automation tries to handle everything. When an issue requires human empathy, negotiation, or broader judgment, the chatbot doesn’t pretend otherwise. Instead, it hands the case to a live agent along with a concise summary of what the customer has already shared and what has been tried so far. That handoff respects the customer’s time and gives the agent a running start.
Straive visualizes this workflow as a loop: identify → analyze → act → escalate → learn. Each interaction feeds back into the system, improving the next one. Over time, automation becomes sharper and more reliable, while humans stay focused on the conversations where their judgment and empathy matter most.
4. Continuous Learning That Makes Support Smarter
Earlier generations of chatbots were essentially frozen in time. Once deployed, they behaved the same way for months or even years, no matter how much the business, its products, or its customers changed. Modern systems are very different. They’re built to learn continuously—adapting to new questions, refining their tone, and evolving as expectations shift. That ongoing learning cycle is what keeps them helpful instead of slowly drifting into irrelevance.
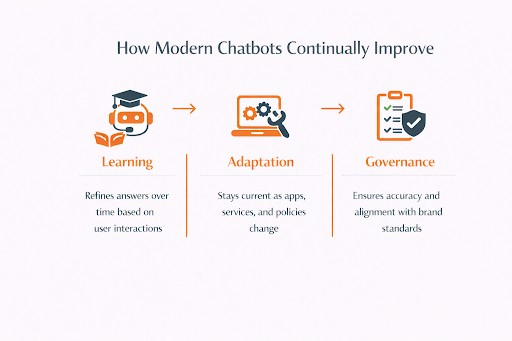
A big part of this comes from staying aligned with real-world changes. When apps, services, or policies are updated, the underlying logic and content that drive the chatbot are refreshed as well. That means it can answer questions about new features, revised pricing, or updated processes without giving outdated guidance. Customers don’t see all of that complexity; they simply experience answers that feel current and reliable.
Behavior also shapes the way these systems evolve. Feedback loops capture what customers respond well to, where they drop off, and which answers lead to follow-up questions or frustration. Over time, this helps the chatbot adjust how it explains things, which options it suggests first, and how much detail it provides. The goal is to become clearer, not just smarter.
Governance is another essential layer. It’s not enough for a system to be quick or clever; it also has to be responsible. Governance checks make sure responses stay accurate, respectful, and aligned with the brand’s standards and values. They help prevent drift into tone or content that doesn’t feel right for the organization.
On top of this, predictive intelligence allows the system to anticipate needs—offering help before a customer runs into a problem or gets stuck in a process. Straive brings all of these elements together in a continuous cycle: Predict → Act → Learn → Optimize. With each turn of that loop, the chatbot becomes more capable and more closely aligned with how customers actually behave, turning it from a static tool into a long-term CX asset.
5. The Trends Shaping AI-Driven Support in 2026 and Beyond
AI in customer support is moving toward a future that feels more ambient, intuitive, and seamlessly woven into everyday interactions. Several emerging trends are already shaping this direction.
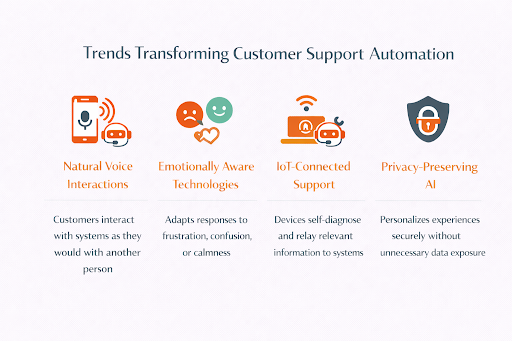
Voice-based interactions are becoming more natural, allowing customers to speak to support systems the way they would to another person. Emotionally aware technologies are improving as well, enabling responses that adjust to a customer’s frustration, confusion, or calmness. This creates interactions that feel more considerate and less mechanical.
IoT-connected support is also gaining momentum. Devices can now diagnose certain issues on their own and share relevant information directly with support systems, reducing the time customers spend troubleshooting. Alongside this, agentic AI is beginning to handle more complex, multi-step tasks—everything from coordinating service appointments to guiding customers through detailed processes—while still maintaining appropriate oversight.
Just as important is the rise of privacy-preserving AI. These advancements allow companies to deliver personalized experiences without compromising security or exposing unnecessary customer data.
Together, these trends signal a shift toward proactive support. Instead of stepping in only after a problem occurs, future systems will anticipate needs, prevent issues, and create a smoother journey long before customers ask for help.
The Balance: Speed, Sensitivity, and Trust
Even with all these advancements, AI chatbots still work best in partnership with people. They can misread tone, overlook cultural nuance, or struggle with situations that require negotiation or reassurance. That’s why live agents remain essential. When you combine the strengths of both, you get support that is fast and efficient without losing warmth or sensitivity.
Privacy is another critical part of the equation. Customers are more aware than ever of how their data is collected, stored, and used. If they feel uncertain or kept in the dark, trust erodes quickly. Being clear about what information is gathered—and why—helps reduce that tension. It shows respect and gives customers confidence that their data is being handled responsibly.
A useful way to think about this is as a “Responsibility Triangle”: technology for efficiency, humans for empathy, and governance for trust. Each side reinforces the others. Businesses that strike this balance are better positioned to set the next standard in customer experience—one that is not only intelligent and responsive, but also human-centered and trustworthy.
Conclusion: Human-Centered Support Enabled by AI
AI chatbots are redefining customer support by making interactions quicker, smoother, and more intuitive. They maintain context, offer multilingual support, automate routine tasks, and grow smarter over time with each interaction. Yet the heart of great service—empathy, clarity, and trust—still comes from people who listen, explain, and make considered decisions.
The most effective customer support strategies in 2026 bring these strengths together. Automation handles the repetitive, time-sensitive work, while human agents focus on complex questions, sensitive moments, and relationship-building. Customers experience less waiting, fewer handoffs, and clearer answers, without feeling like they are talking to a script.
Straive works with organizations to design this kind of balanced model, where technology is guided by thoughtful governance and strong data foundations. In that setup, every chatbot interaction has a purpose: to resolve issues faster, support human teams, and quietly reinforce loyalty with each conversation. Over time, that combination becomes a true, durable competitive advantage.
FAQ’s
They understand context, intent, and can complete multi-step tasks rather than relying on fixed scripts.
No. They take on repetitive work so human agents can focus on nuanced conversations.
Through continuous updates, data validation, and responsible oversight.
Yes. They offer unified, multilingual, omnichannel experiences.
With consent-based data practices, anonymization, and strong encryption.
Voice AI, emotion-aware interactions, predictive support, IoT integration, and privacy-focused learning.